CRE Tech Adoption Speeds Up

Commercial real estate has been a slow adopter of new technology, but that’s about to change.
THE COMMERCIAL real estate industry is reputed to be a slow adopter of digital technology, but with the quickening pace of innovation and the growing sophistication of investors and occupiers, that’s all about to change, according to CRE tech experts. Overall, the term “technology” is used very broadly, and the impact of tech varies greatly among the many disciplines related to CRE. The descriptions below relate to a wide range of computing platforms, software and applications being explored and used by companies involved with all aspects of CRE.
Technology has swept through many businesses, but progress in the commercial real estate industry has been slow in recent years. Today, however, the use of digital platforms and data is accelerating at such a rapid pace that CRE practitioners who fail to fully embrace and understand what is happening will be left behind. Many major brokerage firms and developers have joined the race to invest in technology, which they believe will provide them with a competitive advantage.
Building Design In Transition
Brandon Garrett, AIA, associate/design technology leader at Dekker/Perich/Sabatini, notes that technology is playing a greater role both in his firm’s architectural business and in the commercial buildings that it designs.

Brandon Garrett
Over the past decade, according to Garrett, architects have transitioned from two-dimensional documentation using software like AutoCAD to 3-D building information modeling (BIM). “We are designing our projects virtually to better meet our clients’ needs and to help avoid costly errors during construction,” he explains. “BIM has provided us with a rich model that we can leverage for additional uses such as energy modeling and virtual reality.” Virtual reality also enables prospective tenants to visually inspect “finished space” before a building is actually constructed, allowing them to determine whether the build-out will suit their business. “With virtual reality, we are finding new ways to immerse our clients into projects,” Garrett adds.
One technology that has already arrived with unparalleled impact for the industry is the “internet of things,” the interconnection via the internet of computing devices embedded in everyday objects, according to Garrett. Quoting from a 2014 Goldman Sachs study, “The Internet of Things: Making Sense of the Next Mega-trend,” he predicts that there will be 28 billion connected devices on the IoT by 2020. In commercial buildings, these devices already include sensors that monitor the environment and measure temperature, humidity, water pressure, power consumption and more. He envisions a sensor for virtually everything in a building that an owner or occupier cares to monitor in the near future.


Ted Brown of ReMax Island Properties and Ted Brown Real Estate Inc. (top) and Christian Perlini of Total Real Estate Consultants experience a virtual reality tour of Cypress Creek Medical Pavilion in Fort Lauderdale, Florida. Development partner ANF Group introduced the 360 degree tour, which enabled brokers to navigate through the building’s interior and exterior, at a broker introduction breakfast. Photo at top by Diane Diamantis, courtesy of WordWork PR for Cypress Creek Medical Pavilion; photo at bottom by Gilbert Alvarez, marketing director, ANF Group
These sensors provide new insights into how buildings are actually performing, Garrett notes. “Retail clients will use sensors to generate heat maps of activity to see if their customers are actually approaching product displays. That same information can be used to inform the future placement of displays based on the data being collected.” Today, he adds, the primary use of sensors in commercial buildings is to monitor and control lighting.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence
Sensors can generate data continuously, Garrett notes. This data will increasingly be used by machine learning and artificial intelligence platforms. Google is already using machine learning and artificial intelligence to dramatically lower energy use and costs at its numerous data centers, says Garrett.
To describe just how Google is doing this, he explains that the company has developed AlphaGo, the first computer program to defeat a professional player in the ancient and highly complex Chinese game of Go. Google designed AlphaGo to think and strategize in response to its human opponents.
What does the game of Go have to do with commercial buildings? Google has applied the technological innovations in human intelligence and machine learning that it built into AlphaGo to its data centers. This technology has allowed the company to cut server energy costs by 40 percent, Garrett explains.
“What we will see in the next few years,” the architect forecasts, “is a combination of the internet of things and machine learning, which will revolutionize how buildings are consuming energy.” To optimize a piece of equipment in the future, the IoT and machine learning will not only look at that one piece of equipment; they will also examine thousands of installations of that equipment connected to the internet to optimize its use in a particular setting.
The Developer Perspective
Logistics real estate leader Prologis offers a look at how it is using new technologies throughout its portfolio and how it expects to deploy them in the future. Tom Sheraden, the company’s chief information officer, points to three areas of technology – the internet of things, cloud storage and artificial intelligence – that are rapidly being adopted today, as well as a fourth, blockchain, that will have a profound impact in the future.

Tom Sheraden
“If your building could talk, what would it say?” asks Sheraden. “The reality is that our buildings can tell us a lot, once we install sensors in them. They have the capacity to tell rich stories about how the buildings are operating and how they are being used.”
Thanks to the IoT, explains Sheraden, the same technologies that are launching a revolution across other industries will allow building owners and occupants to capture more data than ever on how goods flow through buildings. “These insights will help our customers make smarter decisions on everything from energy use to overall sustainability, efficiency and employee health and well-being.” He adds that Prologis’ large scale creates unique opportunities for the company to collect huge amounts of data over long periods of time and incorporate it into advanced analytics analyses that will benefit its customers.
Prologis already uses sensors to “inform our efforts in sustainability and efficiency – monitoring solar panel operation and measuring air quality,” Sheraden continues. In the future, Prologis could use sensors across its operations, providing customers with predictive data insights to help drive their businesses and operations. For example, sensor data could identify when and where building maintenance is needed, helping improve operations, boost safety and lower costs. Building owners will also be able to provide space optimization and utilization recommendations to customers more quickly and cost effectively.
“On a broader scale,” Sheraden adds, “customers could use data insights to benchmark themselves against the industry and identify strengths and weaknesses in their operations.”
Storing Big Data
While the IoT will help developers and occupiers gather incredible amounts of information, how and where will they store all that data? “Historically,” says Sheraden, “it has been very expensive to acquire data, structure it and store it. “ Today, Amazon, Microsoft and Google are all “delivering cloud-based data platforms that essentially let you pay as you go,” Sheraden adds.
This cost savings allows a CRE company to save all of the data it collects, then figure out how to use that data later. A company can therefore accumulate huge amounts of data and then examine it “for patterns and relationships that will help you as a business move faster and serve customers better,” Sheraden concludes.
CRE: Still a Relationship Business
While these technologies will have dramatic impacts on CRE, Chandra Dhandapani, chief digital and technology officer at CBRE, says that commercial real estate will continue to be a relationship-based business. She notes that people can now purchase products and services through numerous channels, in what is typically referred to as an omnichannel experience. In CRE, she adds, “we go through one channel, the human channel, what I call the phone-a-friend channel. Clients usually interact with CRE professionals, and that’s how a transaction is made in this industry.”

Chandra Dhandapani
Dhandapani stresses that clients rely on trust to ensure that they are being properly advised and guided by those with whom they have professional relationships. In the future, she concedes, these relationships could involve more digitally enabled interactions. But those interactions will still be relationship based.
She adds that CBRE views technology along three dimensions. First, technology needs to solve an existing problem, rather than be treated as a solution in search of a problem, as is often the case. Second, technology is presenting CRE with a tremendous opportunity for growth, not simply innovation that leads to disruption. Third, companies that are able to leverage technology will quickly separate themselves from their less tech-savvy competition.
With more information available in the future, CRE developers and occupiers will be better able to make smarter location decisions, according to Dhandapani. “For office buildings, for example, you want a location where you have the most access to the right kind of talent and the right amenities for those people. Today, much of that process is manual. In the future, you will be able to do many of those things [more easily] with the right technologies.”
Will Tech Level the Playing Field?
Will big data, cloud computing, the IoT and sensors that monitor virtually everything in a building help or hinder smaller developers, investors and property owners? According to Dhandapani, they are likely to help the smaller player. “The beauty of what people are referring to as the digital economy is that while scale obviously helps, it is not always required to win. There are a number of successful examples of small start-ups with six to eight people adding tremendous value in whatever industry they are in. I think size is beginning to matter less in this economy, and many of the technologies are either free or [available] at a much lower cost than in the past. You don’t have to spend millions of dollars to build cutting-edge technology today. If you are a smaller developer … you can find the best way to solve [a problem] with technology without having to spend the kind of money that large companies have to spend.”
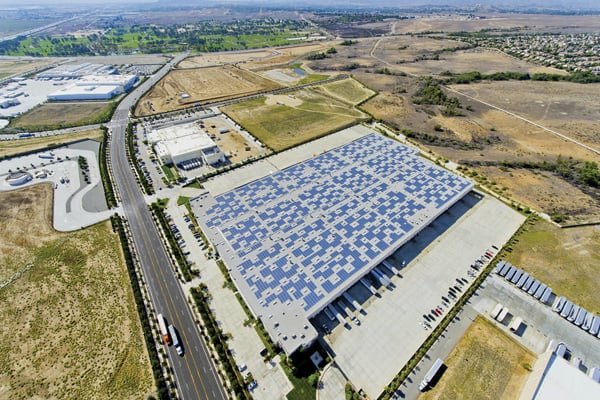

Prologis partnered with Bright Plain Renewables and D.E. Shaw Renewable Investments to design and build solar plants at Prologis-owned warehouses in Southern California. The three sustainably designed warehouses total over 1.3 million square feet and produce an estimated 9.8 kilowatt hours per year. D.E. Shaw owns the solar installations and leases roof space from Prologis, which uses sensors to monitor solar panel operation and measure air quality. Photo courtesy of Prologis
Prologis’ Sheraden sees it differently. While every CRE professional must consider their own specific business case, he feels that scale is critical when it comes to technology. “This is why Prologis is uniquely positioned to take advantage of big data in our business. New technologies can improve efficiency in a single building, but the value rises exponentially with a network of facilities sharing information. Smaller developers might be able to mimic scale by partnering with other companies to share data, but a network is critical to drive insights for customers.”
Will all of this new technological innovation become merely “table stakes” in the future? According to Sheraden, “The technologies themselves will inevitably become table stakes, but in the near term they will allow some [CRE practitioners] to stand out from the competition.” Sheraden concludes that what matters most “is serving our customers and being a partner in their success. That won’t go out of style.”
Ron Derven is a contributing editor and Margarita Foster is editor-in-chief of Development magazine.
A Primer on New TechnologiesRapidly developing technologies are cutting into the costs of designing, developing and operating buildings as well as carrying out transactions, incentivizing CRE professionals to increase the speed of adoption. Industry experts expect the following six technologies to have an impact on CRE in the near future: The Internet of Things. The internet now connects sensors and other computing devices embedded in everyday items, from home washing machines to commercial HVAC systems. Many of these devices can be programmed to send and/or receive data daily, hourly or even continuously. Big Data. The IoT is enabling the collection and storage of extremely large data sets, which can be collected and analyzed, both independently and in conjunction with other data sets, to reveal patterns, trends and associations. Cloud Computing. Many companies and individuals now use a network of remote servers connected via the internet to store, manage and process data, rather than storing it all on their own local servers or personal computers. Virtual and Augmented Reality. Computer-generated 3-D simulations and 3-D videos enable people to virtually “tour” properties remotely and even “visit” and “feel” projects still in the early stages of design or construction, using special equipment such as 3-D cameras, goggles and/or gloves. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning. Computer systems can now perform many tasks that in the past would have required intervention from a human programmer. Some can also learn to make adjustments to changing circumstances, based on experience, without being explicitly programmed to do so. Blockchain. This public digital ledger is similar to a relational database that stores transaction records in a series of chronologically connected “blocks.” For example, if ownership of an asset is transferred on a blockchain platform from one party to another, the exchange is time stamped, sealed in a block and chronologically linked to previous transactions related to the asset. This process creates verified transactions with a clear timeline that cannot be pulled apart. |